 In this article we’ll discuss the possible impact from the handling of 404 errors. These are caused by requests to pages or resources that don’t exist on the server.
In this article we’ll discuss the possible impact from the handling of 404 errors. These are caused by requests to pages or resources that don’t exist on the server.
By default a lot of the applications you might install on your website, will try to process requests for a page that doesn’t exist dynamically.
What this can mean, is each time someone mistypes a URL, your application is going to query the database to try to figure out if that page exists, and if it doesn’t it’s going to serve up a page not found error to the visitor.
In most cases this type of default 404 error page activity is completely harmless. However as the amount of 404 error pages you’re forcing the server to think about increases, it can become more and more problematic.
Causes of 404 Errors
Let’s take a look at some of the most common reasons a 404 error might be generated.
- A visitor tries to manually type in a page that doesn’t exist.
- Your pages were not internally or externally linked correctly in the first place.
- Resources such as images, .css, .js, or other files were removed from the server.
- One of your pages was moved, and links either internal or external weren’t updated.
- Search engine crawlers, or automated bots try to access generic pages that your site doesn’t have.
404 Error Page Handling
A good webmaster will want to periodically check on their website statistics to see what requests are generating the most 404 errors.
You can use this information to your advantage, as lets say for example you notice 500 people a month are trying to pull up a page called /about that doesn’t exist. You can go ahead then and create that page, or setup re-direction on that URL to hopefully get them pointed in the right direction and have them remain on your site during future visits.
Viewing 404 Errors via Awstats
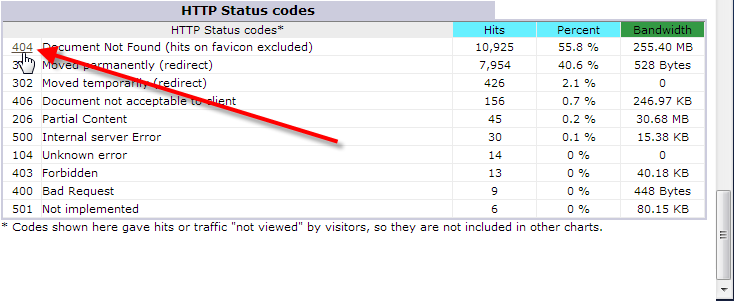
You can view your 404 errors via Awstats from within cPanel.
Once you’re logged into Awstats, if you simply scroll to the very bottom of your statistics report, you should see the total number of 404s encountered and what percentage of your traffic that represents.
Then simply click on the 404 link to see the actual requests triggering these errors.
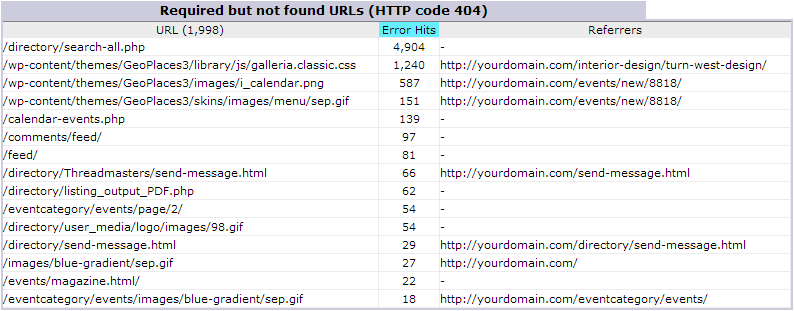
In this example you can clearly see that the URL /directory/search-all.php is by far the biggest cause of the 404 errors on this site.
You can also see that there are several resources such as .css stylesheets and .png and .gif images that are missing.
Note the Referrer of these resources, as those would be the pages with the invalid links to these files that don’t exist.
Creating Static Custom 404 Error Pages and Handling Excessive Requests
Now that we’ve seen a little bit about what a 404 error is, you might wish to dive deeper and configure a custom 404 error page to help steer your visitors to other sections of your site when then try to access a page that doesn’t exist.
Or if you’re having problems with too many 404 errors causing performance issues a static 404 error page can help with this as well. All of the following articles go more in-depth on handling 404 errors and would be recommended reading for anyone looking to get the total big picture on 404 error handling.

My Pages Not Found today lists 368 type 404 errors. 146 were from one IP. It is an education network which of course does not identify its clients Many users would not be particularly familiar with the stringent naming systems in internet activity. 71 are .js files and 47 are .css files; these do not exist on my web page. So there can be systematic (i.e. big) errors “out there” that result in attempts to find files that do not exist on one’s website.
Hello Michael, and thank you for your comment.
If you are experiencing a large amount of 404 errors from a particular IP address, or a particular User-Agent string, you could use some .htaccess deny rules to block their access.
If you are seeing a large amount of requests for .js or .css files not being found, you might want to double-check to ensure the referring URL the user was on isn’t making their web-browser try to request those non-existent files because of your HTML code itself.
You can also use .htaccess rules to block a particular page from being requested if you keep seeing the same one happen. For instance if the file 404.js kept getting requested, and you’ve verified it is not your code calling it, and that the file doesn’t exist. You could then use this bit of code in your .htaccess file to deny any requests for it:
RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} ^/404.js$ RewriteRule .* - [F,L]Thanks again for your comment, and let us know if you have any questions at all!
– Jacob